GlucoSense
The Need
Over 380 million people in the world suffer from Diabetes Mellitus, and its prevalence is expected to double in the next decade. The most common method of self monitoring requires invasive finger pricking, which can be painful and lead to bruising, loss of sensitivity in the affected nerves, and blood-borne infections. Alternative solutions based on optical technologies are expensive. There is demand for a glucose monitoring method that is more comfortable for patients.
The Project
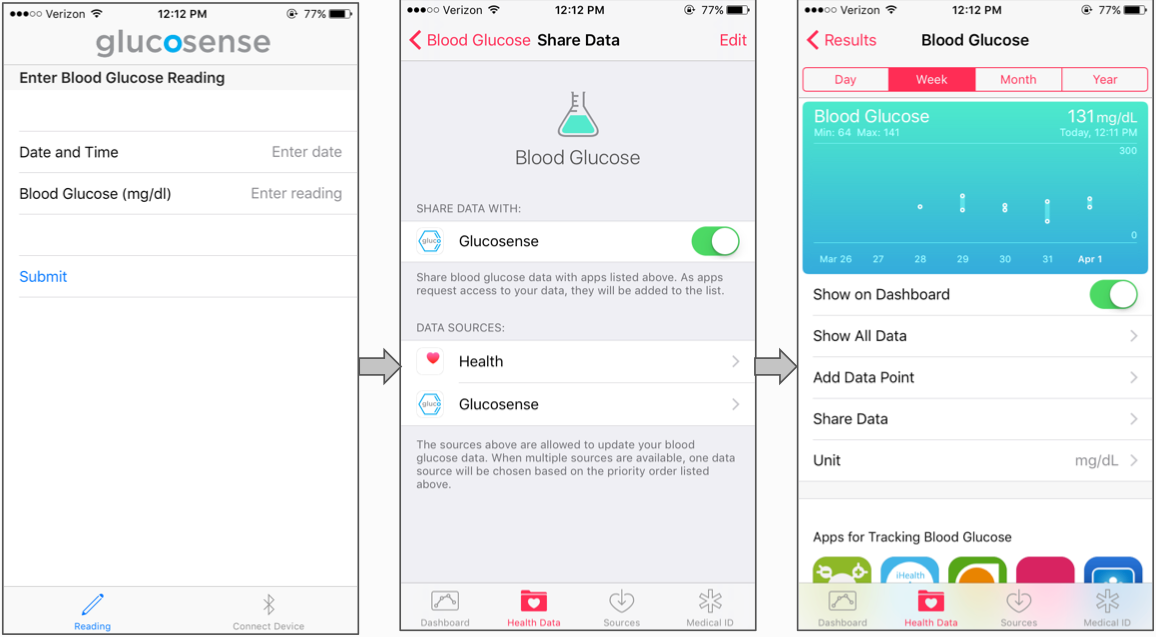
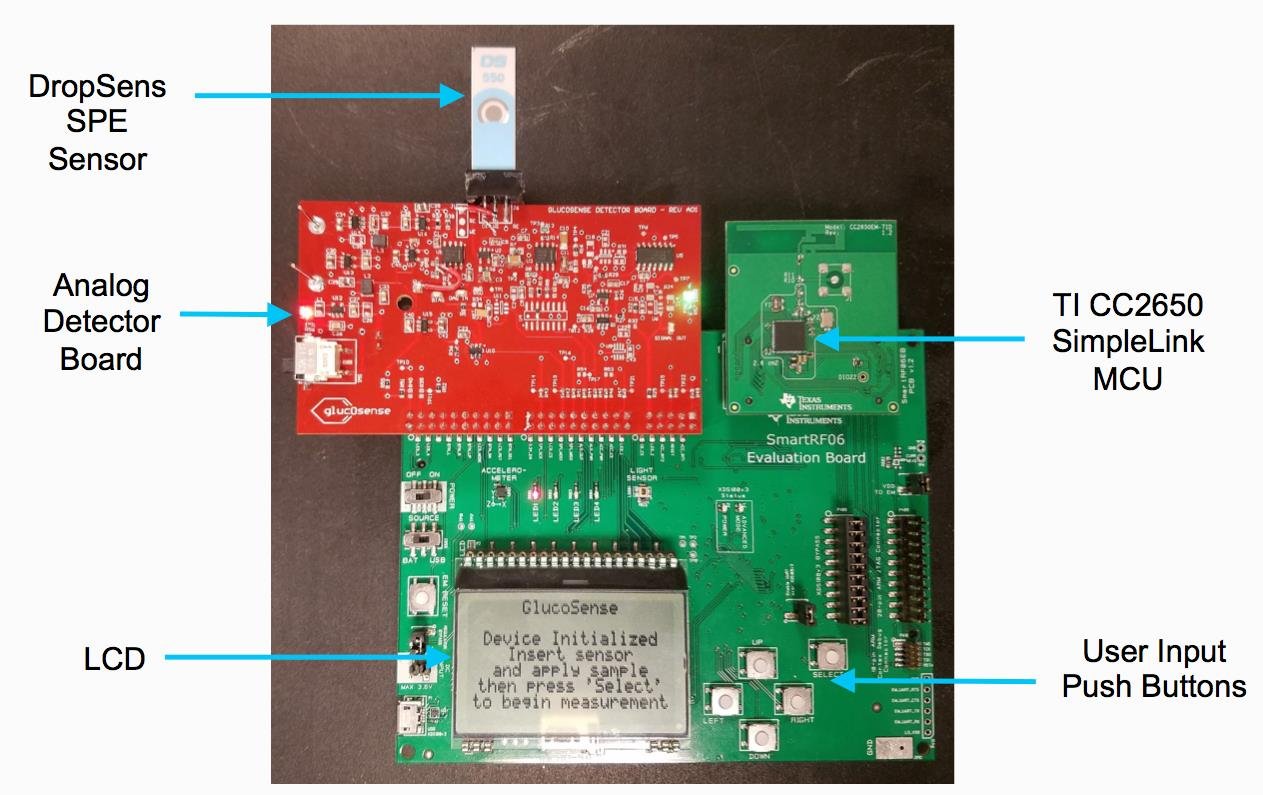
This project measures glucose concentration from a saliva sample detected by a biosensor developed by Prof. Wang. The design uses a potentiostat circuit that interfaces with the sensor and performs an amperometric measurement by applying a constant bias potential between the working and reference electrodes via a digital-to-analog converter. The sensor signal is conditioned through a three-stage amplifier and a filtering circuit that helps achieve high resolution. The signal is sampled and integrated in firmware to acquire a current density that is linearly proportional to the concentration of glucose present in the saliva sample applied. The correlated salivary glucose concentration is then displayed on the LCD. An iOS app was developed that takes in a user’s correlated blood glucose level and interfaces with Apple’s HealthKit to provide secure data storage and features such as temporal plots and sharing of glucose readings with family members and health professionals.
Current Status
The project is complete and the project won a prize at the 2016 ECE Design Competition.